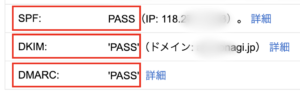
更新:PHP8.2からPHP8.3へ変更しました。 PHP8.2の場合は 8.3を8.2に置き換えるだけです。
CentOSでApache, PHP 8.3 (PHP-FPM) とMariaDBを使用してセキュアなWEBサーバーを構築する手順は以下の通りです。
この手順を作成した環境は AlmaLinux9.2 です。
例示のドメインとして example.com を使用しています。自組織のドメインに置き換えてください。
システムのアップデート
まず、システムをアップデートしておきましょう。
sudo yum -y update
EPELリポジトリとRemiリポジトリの追加
EPELリポジトリとRemiリポジトリを追加し、最新バージョンのPHPをインストールできるようにします。
※2024年12月18日時点では 9.2があります。
sudo yum -y install epel-release
sudo yum -y install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-9.2.rpm
Apacheのインストール
まず最初にApacheとmod_ssl(セキュア接続用のモジュール)をインストールします。
自動起動設定を行い、起動します。
sudo yum -y install httpd mod_ssl
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl start httpd証明書の設定
Apache用のサーバー証明書を自己署名(Self-Signed Certificate)で作成する手順を以下に示します。これは開発環境やテスト環境で利用されますが、本番環境ではLet’s Encrypt(無料) や グローバルサイン等の公認認証局(CA)から証明書を取得することをお勧めします。
グローバルサイン
外部リンク: https://jp.globalsign.com/

OpenSSL のインストール
自己署名証明書を作成するために、OpenSSL をインストールします。
sudo yum -y install openssl秘密鍵と自己署名証明書の生成
/etc/pki/tls/private ディレクトリに秘密鍵を作成し、 /etc/pki/tls/certs ディレクトリに自己署名証明書を作成します。
sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/pki/tls/private/apache-selfsigned.key -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/apache-selfsigned.crt
証明書情報を入力してください。
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:JP
State or Province Name (full name) []:Tokyo
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Shibuya-ku
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Example Company
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Web Department
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:example.com
Email Address []:email@example.com
Apache の設定を変更して、自己署名証明書を使用するようにします。
/etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.confファイルを開いて、以下のように設定を変更します。
sudo vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
# SSLCertificateFile の設定
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/apache-selfsigned.crt
# SSLCertificateKeyFile の設定
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/apache-selfsigned.key
設定ファイルの変更が終わったら保存し、閉じます。
VirtualHostの設定
ApacheのVirtualHostとは、1つのApacheウェブサーバー上で複数のドメインやサブドメインをホストするために使用される機能です。これによって、1つの物理的なサーバーに異なるWebサイトやアプリケーションを配置して、各ドメインやサブドメインごとに異なる設定や振る舞いを適用することができます。
名前ベースの VirtualHostとIPアドレスベースの VirtualHostがありますが、ここでは一般的に使用されている名前ベースの VirtualHostで設定を行います。
複数のユーザーが使用する前提で、ドキュメントルート(公開ディレクトリー)とログディレクトリーは、ホームディレクトリーの下に作成するようにしています。
ここでは、 taro というユーザーの設定としています。
ViatualHost毎に必要なディレクトリーを作成しておきます。
sudo mkdir -p /home/taro/example.com/logs
sudo mkdir -p /home/taro/example.com/public_html
sudo chmd 0705 /home/taro/etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.confという新しいファイルを作成し、以下の内容でVirtualHostブロックを設定します。
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin admin@example.com
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
DocumentRoot /home/taro/example.com/public_html
ErrorLog /home/taro/example.com/logs/error.log
CustomLog /home/taro/example.com/logs/access.log combined
Redirect permanent / https://example.com/
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost _default_:443>
ServerAdmin admin@example.com
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
DocumentRoot /home/taro/example.com/public_html
ErrorLog /home/taro/example.com/logs/ssl_error.log
CustomLog /home/taro/example.com/logs/ssl_access.log combined
SSLEngine on
SSLProtocol All -SSLv2 -SSLv3 -TLSv1 -TLSv1.1
SSLCipherSuite ECDH+AESGCM:DH+AESGCM:ECDH+AES256:DH+AES256:ECDH+AES128:DH+AES:ECDH
+3DES:DH+3DES:RSA+AESGCM:RSA+AES:RSA+3DES:!aNULL:!MD5:!DSS
SSLHonorCipherOrder on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/apache-selfsigned.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/apache-selfsigned.key
# Let's Encrypt 証明書を使用する場合は、中間証明書(chain.pem)を設定
# SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/chain.pem
Protocols h2 http/1.1
<Directory /home/taro/example.com/public_html>
Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
この設定では、HTTPリクエストを自動的にHTTPSにリダイレクトし、公開ディレクトリが /home/taro/example.com/public_html に設定されています。ドキュメントルートやドメイン名は適宜変更してください。
ApacheでAH01630エラーがでる場合は、以下の設定がどこかに残っていないか確認します。
# Apache2.2以前の設定
Order allow,deny
Allow from all# Apache2.4以降の設定
Require all grantedPHP 8.3とPHP-FPMのインストール
PHP 8.3およびPHP-FPM等のPHP および必要な拡張機能のパッケージをインストールします。
remi-safeリポジトリを有効にします。
sudo yum -y install yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager --enable remi-safe
yum のモジュールをリセットし、remi-modular リポジトリから PHP 8.3 をインストールします。
sudo dnf module reset php
sudo dnf module enable php:remi-8.3
PHP および必要な拡張機能をインストールします。
sudo yum update
sudo yum -y install php php-cli php-fpm php-common php-mysql php-gd php-xml php-mbstring php-json
PHP-FPMの設定
必要に応じて、PHP-FPMの設定ファイルを編集します。
sudo vi /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
Apacheの動作ユーザーとグループが規定値で apache として設定されています。
特定のユーザーやnobody権限で動作させたい場合は、 user と group の項目を変更してください。
; Unix user/group of processes
; Note: The user is mandatory. If the group is not set, the default user's group
; will be used.
; RPM: apache user chosen to provide access to the same directories as httpd
user = apache
; RPM: Keep a group allowed to write in log dir.
group = apache
設定が完了したら、PHP-FPMを自動起動設定し、起動します。
sudo systemctl enable php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php-fpm
ApacheでPHP-FPMを有効にする
ApacheでPHP-FPMを有効にするために、/etc/httpd/conf.d/php.conf を編集します。
sudo vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/php.conf
必要に応じて PHP-FPMの設定を変更してください。
規定値で、以下のように設定されているのでそのままでも問題ありません。
# Redirect to local php-fpm if mod_php (5 or 7) is not available
<IfModule !mod_php5.c>
<IfModule !mod_php7.c>
<IfModule !mod_php.c>
# Enable http authorization headers
SetEnvIfNoCase ^Authorization$ "(.+)" HTTP_AUTHORIZATION=$1
<FilesMatch \.(php|phar)$>
SetHandler "proxy:unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock|fcgi://localhost"
</FilesMatch>
</IfModule>
</IfModule>
</IfModule>Apacheを再起動して、変更を反映します。
sudo systemctl restart httpd
SELinuxの設定 (オプション)
SELinuxが有効な場合、HTTP通信を許可する設定を行います。
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db 1
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1
これで、Apache, PHP 8.2 (PHP-FPM) とMariaDBを使用したセキュアなWEBサーバーが構築されました。次に、適切なファイアウォールの設定やSSL証明書の設定を行い、完全にセキュアな状態にします。
Firewalldの設定
Firewalldをインストールし、有効化します。
sudo yum install firewalld
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo systemctl enable firewalld
次に、HTTPおよびHTTPSのルールを追加し、ポート80と443を開放します。
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=https --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Let’s Encryptの導入
Let’s Encryptの導入については、下記の投稿を参考にしてください。

ドメイン名が設定されていることを確認し、Apacheの設定に適切なドメイン名が使用されていることを確認してください。
それから以下のコマンドでSSL証明書を取得し、設定ファイルに自動的に適用します。
sudo certbot --apache -d example.com -d www.example.com
以下のような手順になりますが、実際の出力は異なるかもしれません。
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices)
(Enter 'c' to cancel): email@example.com
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Please read the Terms of Service at
https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.3-September-21-2022.pdf. You must
agree in order to register with the ACME server. Do you agree?
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
(Y)es/(N)o: Y
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Would you be willing, once your first certificate is successfully issued, to
share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding
partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that
develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web,
EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom.
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
(Y)es/(N)o: Y
Account registered.
Requesting a certificate for example.com
Successfully received certificate.
Certificate is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem
Key is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem
This certificate expires on 2023-09-07.
These files will be updated when the certificate renews.
Certbot has set up a scheduled task to automatically renew this certificate in the background.
Deploying certificate
Successfully deployed certificate for example.com to /etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled HTTPS on https://example.com
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
* Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
* Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
このコマンドでは、example.comとwww.example.comの両方のドメイン名に対する証明書を取得します。適切なドメイン名に置き換えて実行してください。
/etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf に設定が追加されるので、必要に応じて修正してください。
Let’s Encryptの中間証明書(Intermediate Certificate)
Let’s Encryptの中間証明書(Intermediate Certificate)をApacheウェブサーバーに設定する手順は以下の通りです。これにより、エンドユーザのブラウザが信頼できるルート証明書から連結された証明書チェーンを確立できます。
Let’s Encryptの中間証明書 chain.pemファイルは、証明書を取得したときに自動的に生成されます。このファイルは通常、/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/ディレクトリに保存されています。yourdomain.comは実際のドメイン名に置き換えてください。以下の手順でchain.pemファイルへアクセスできます。
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/
Apache VirtualHost の設定に中間証明書を設定
SSL設定を含むApacheのVirtualHost設定ファイルを開きます。VirtualHost設定ファイルが別々に保存されている場合(例:/etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf)、そのファイルを開きます。
sudo vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf
SSL設定が含まれるVirtualHostセクションに、以下の設定を追加または編集します。yourdomain.comは実際のドメイン名に置き換えてください。
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName example.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/example.com
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/cert.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem
SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/chain.pem
ErrorLog logs/example.com-error_log
CustomLog logs/example.com-access_log combined
</VirtualHost>
Apacheの設定を更新し、サービスを再起動します。これにより、Let’s Encrypt SSL証明書が適用されます。
Apacheを再起動して、変更を反映します。
sudo systemctl restart httpd
ログローテーションの設定
Webサーバーのログの保存場所は、ご自身の環境に合わせて調整してください。
ここでは、以下のようなパターンで設置されている前提です。
/home/httpd/example.net/logs/access_log
/home/httpd/example.net/logs/error_log
/home/httpd/example.com/logs/access_log
/home/httpd/example.com/logs/error_log
logrotate.d の設定
sudo vi /etc/logrotate.d/httpd/home/*/logs/*log {
daily
rotate 30
compress
delaycompress
missingok
notifempty
create 0644 root root
sharedscripts
postrotate
if systemctl is-active --quiet httpd.service; then
systemctl reload httpd.service > /dev/null 2>/dev/null || true
fi
endscript
dateext
dateformat -%Y%m%d.gz
}具体的な内容は以下の通りです。
/home/*/logs/*logこれは対象となるログファイルのパスを示しています。*/logs/*log というパターンのパスにマッチするすべてのログファイルが対象となります。dailyログローテーションを毎日行います。rotate 3030 回目のローテーション後、最も古いログファイルが削除されます。compress2 回目以降のローテーションから圧縮します。delaycompress圧縮は次のローテーションまで延期されます。つまり、2つ前のログファイルから圧縮します。missingokログファイルが存在しなくてもエラーになりません。notifemptyログファイルが空の場合はローテーションしません。create 0644 root root新しいログファイルを作成します。所有者とグループは root に、ファイルのパーミッションは 0644 に設定されます。sharedscriptsローテーションはすべてのログファイルが処理された後に一度だけ行います。postrotate…endscriptログファイルがローテーションされた後に実行されるスクリプトです。この例では、httpd サービスが稼働していれば reload コマンドを実行します。dateextロギングローテート時に現在の日期を接尾辞として追加します。dateformat -%Y%m%d.gzログファイルの接尾辞として使用する日付のフォーマットを設定します。この例では年月日(例: -20220301.gz)となります。